# Props
# Overview
Native Flutter widgets receive data from their host widgets using constructor parameters.
ezFlap widgets use Props instead.
A Prop is similar to a constructor parameter, only that instead of being specified in a constructor - it is specified
as a field in the widget class, and marked with the @EzProp annotation.
# Example

Then, the ezFlap widget in the example above, can be hosted in other ezFlap widgets:
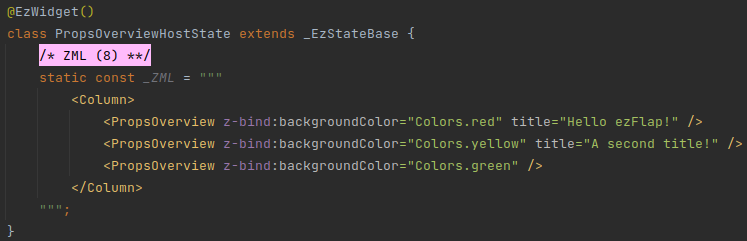
In the above example, the PropsOverview ezFlap widget will be rendered three times, with a different background color and title each time.
It is also possible to pass data to Props using named parameter tags:

KEYS
When the hosted widget passes a key using the z-bind:key or key attributes, if the constructor of the hosted
widget's non-state class (i.e. the class that extends EzStatefulWidgetBase) accepts a key named parameter - then
the key provided by the host widget is passed to the constructor.
If a key prop exists as well - the key is also passed to it.
REMEMBER TO IMPORT
Remember to import the classes of the ezFlap widgets you use.
If they are not imported - the code generator will log errors and generate incorrect code.
USE IN NATIVE FLUTTER WIDGETS
ezFlap widgets can be hosted in native Flutter widgets.
If:
- You want to gradually add ezFlap to an existing codebase.
- Or, you want to author ezFlap widgets that will also be usable in native Flutter widgets.
Then read more about ezFlap Interoperability.
# Reactivity
Props are reactive.
Props are read-only inside the ezFlap widget where they are defined.
Their values change when the values of the attributes that are assigned to them in the host widget change.
# Example
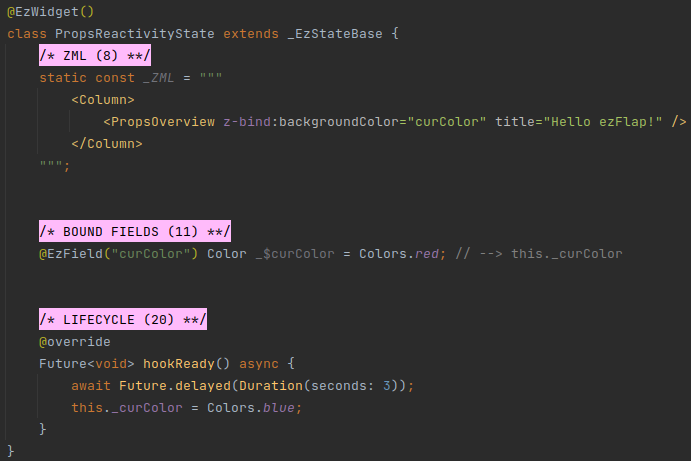
In the above example, the background color of PropsOverview changes after three seconds from red to blue.
# Syntax
Props can be declared in three variations: late, Nullable, and Default Value.
# late
# Example

Like late Bound Fields, late Props must not be accessed before they are made available by the host widget.
# Nullable
Props can be declared as nullable.
# Example
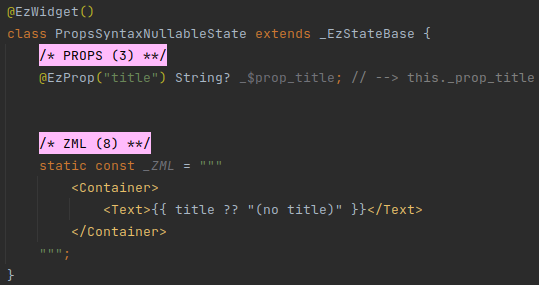
When a Prop is declared as nullable, the same rules that regular Dart nullable rules apply to it.
# Default Value
Props can have a default value.
When a prop has a default value - if the host doesn't pass a value to it - the default value is used.
# Example
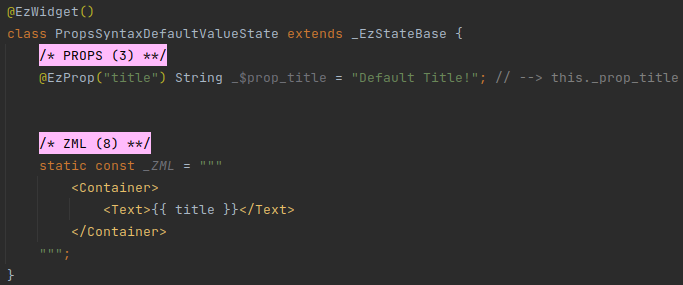
# Conventions
Strongly-recommended conventions that may become mandatory in a future version:
- The prop's Assigned Name (the name provided as parameter to the
@EzPropannotation) should be in camelCase. - The prop's name should begin with
_$prop_, followed by the Assigned Name.
Optional suggested conventions:
- Place the
@EzPropannotation at the same line as the declaration. - Add a
// --> this._prop_<Assigned Name>comment at the end of every field declaration. - Use Live Templates to generate prop declarations quickly and consistently, and without having to remember the syntax.
# Usage
Props can be used in the same places where bound fields and other reactive data can be used.
When used in code, a prop is accessed using the Derived Name of its declaration.
The Derived Name is the text following the _$, prefixed with an underscore.
For example, the Derived Name of:
@EzProp("title") String? _$prop_title;
Would be _prop_title.
The Derived Name of:
@EzProp("title") String? _$superCustomName;
Would be _superCustomName.
← Transformers Events →