# Bound Methods
# Overview
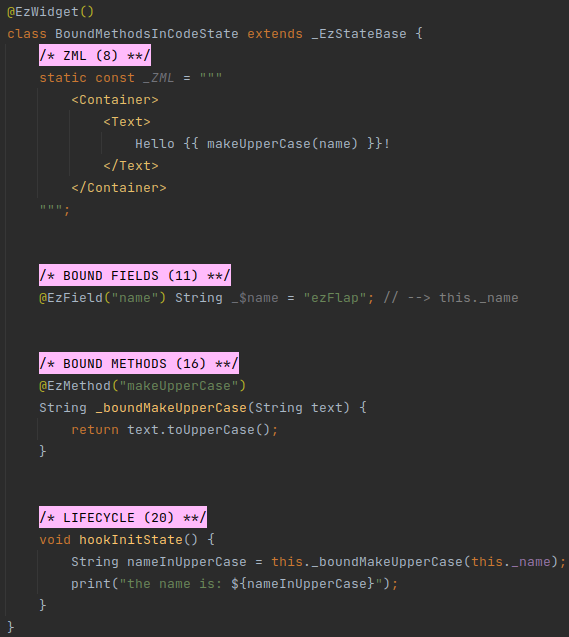
Bound Methods are methods with the @EzMethod annotation.
# Example
- Bound methods are accessible in the ZML.
- Unlike computed methods, the value returned from bound methods is not cached.
- Bound methods may return a value, but can also have a
voidreturn type. - Bound methods may accept parameters.
- Bound methods are never asynchronous.
Bound methods are useful in these scenarios:
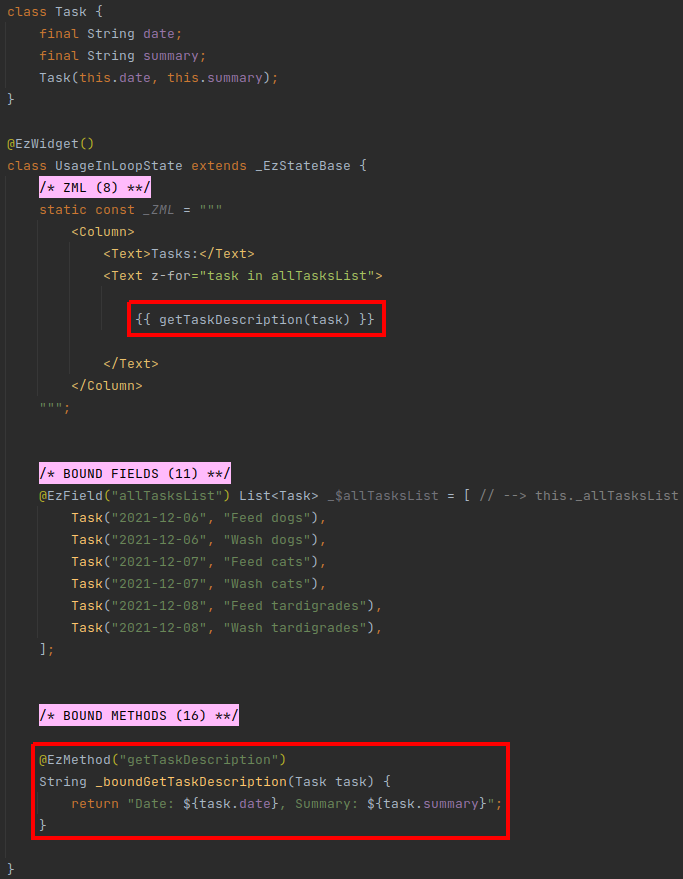
- Retrieve or calculate a value that depends on parameters (e.g. inside a
z-forloop). - Assign bound methods to handle events as the user interacts with the UI (covered in z-on).
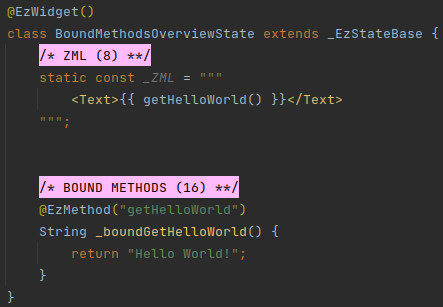
# Example
# Reactivity
Bound methods are reactive.
Bound methods can access reactive data (e.g. bound fields, computed methods) in order to generate their return value or perform other actions (when invoked to handle an event).
Whenever underlying reactive data changes - the widget's build() method is invoked, and consequently, the bound
method is also invoked if needed (e.g. if it's referenced in the rendered ZML in a text interpolation or a z-bind).
The reactivity rules of bound methods are similar to those of computed methods (except that the return value of bound methods is not cached).
For a recap on computed methods reactivity - see Computed Methods Reactivity.
# Syntax
Bound methods are written like regular Dart methods, and are prefixed with the @EzMethod annotation.
The @EzMethod annotation accepts a single parameter: the Assigned Name of the bound method, which will be used
in the ZML to invoke the bound method, or assign it as an event handler (covered in
z-on).
In the ZML, bound methods are referenced with their Assigned Name.
Unlike computed methods, bound methods can appear in the ZML with or without parentheses.
Both options are valid, but have different results, which also depend on where in the ZML the bound method is referenced.
All the variations are covered below, under Usage.
# Example

# Conventions
Strongly-recommended conventions that may become mandatory in a future version:
- The bound method's Assigned Name (the name provided as parameter to the
@EzMethodannotation) should be in camelCase.
Optional suggested conventions:
- Place the
@EzMethodabove the method declaration. - Prefix the bound method's method name with
_bound(e.g._boundGetTaskDescription()). - Use Live Templates to generate bound method declarations quickly and consistently, and without having to remember the syntax.
# Usage
Bound methods can be accessed in z-on, z-bind Dart expressions, named parameters, text interpolation, and regular
code.
AVOID SIDE EFFECTS
When used as event handlers - bound methods may freely update state, save data, etc.
When used to retrieve or calculate data to be displayed in interpolated text or passed to another widget using z-bind,
such actions are considered side effects, and should be avoided.
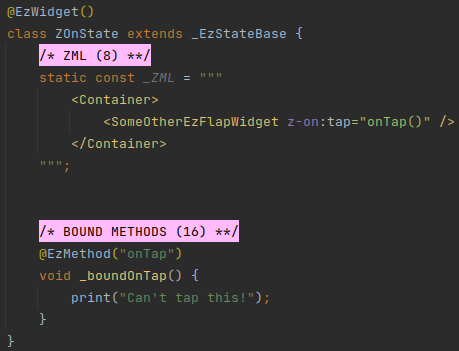
# Usage in z-on
The usage of bound methods in z-on is covered in full in z-on.
This section doesn't go into details because Events have not been introduced yet.
The z-on attribute can only appear on ezFlap widgets. Its purpose is to assign an event handler to an event.
The bound method will be provided to the z-on attribute on its own (i.e. not as part of a longer expression), and
may or may not have parentheses (with some difference in behavior).
# Example
# Usage in z-bind
z-bind attributes accept a Dart expression.
Reference bound methods in these Dart expressions using the bound methods' Assigned Names.
# Example 1 - pass Bound Method in z-bind
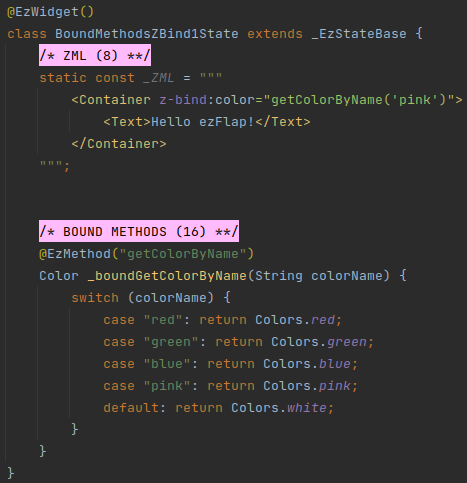
In the above example, the background color of the Container will be pink.
# Example 2 - pass Bound Method in z-bind in loop
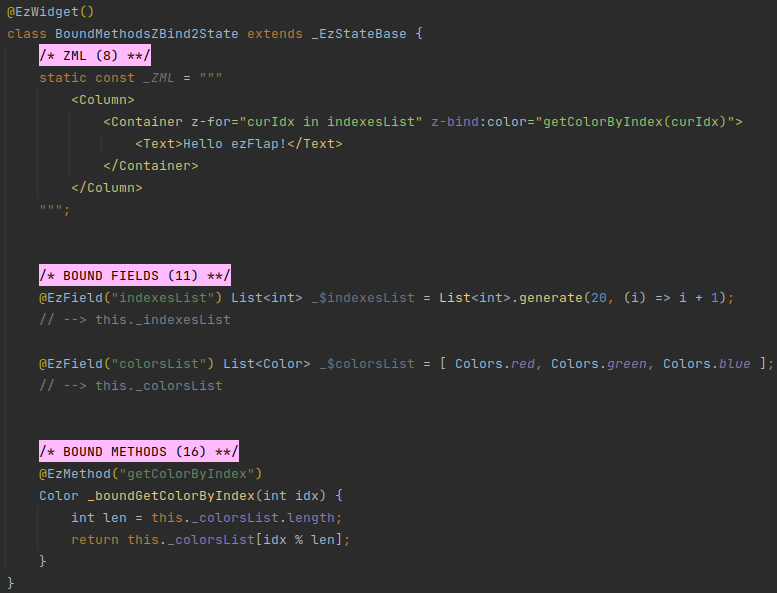
The above example renders a strip of Hello ezFlap! with in repeating red, green, and blue backgrounds.
# Example 3 - Bound Method Without Parentheses in z-bind
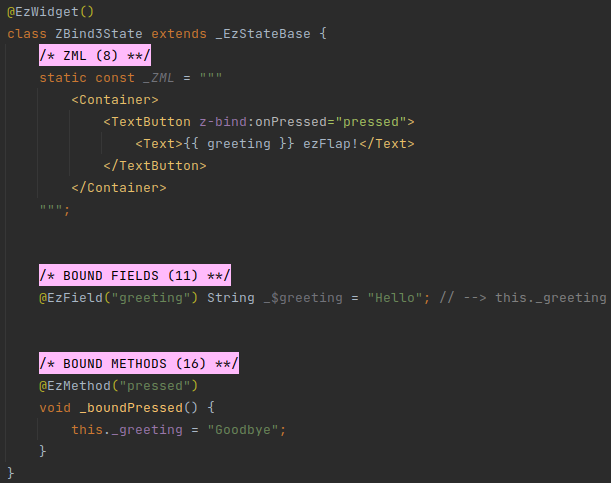
In the above example, z-bind:onPressed="pressed" doesn't cause pressed to be invoked when the ZML is rendered,
because there are no parentheses after pressed. Instead, ezFlap passes the pressed method in TextButton's
onPressed named parameter.
When the user presses the "Hello ezFlap!" greeting - the pressed bound method is invoked, and the displayed text
changes to "Goodbye ezFlap!".
# Example 4 - pass Bound Method in z-bind in loop - Advanced Scenario
Suppose that we have multiple TextButtons, rendered in a loop, each with a counter in its caption.
And suppose that we want a press on each of them to increase its own counter.
We can implement this by creating a bound method that returns a method:
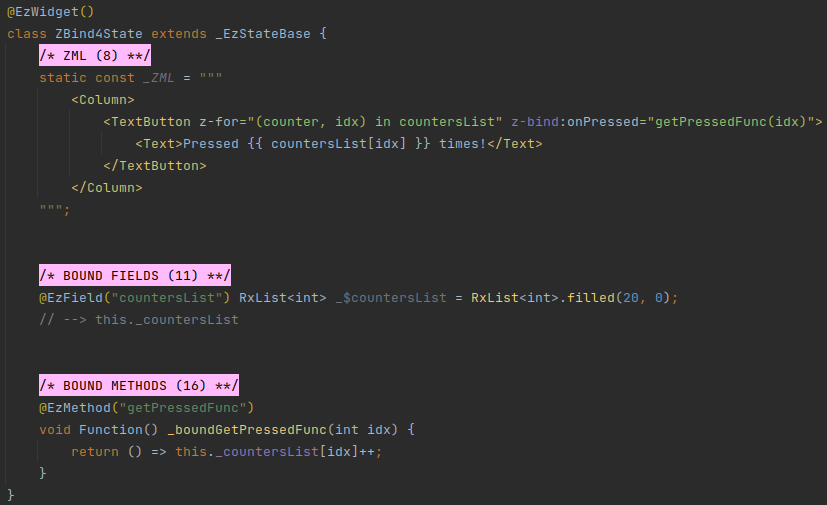
A BETTER WAY
There is a better way to do such things, and avoid creating a bound method that returns a function, by using ezFlap Widgets and z-on.
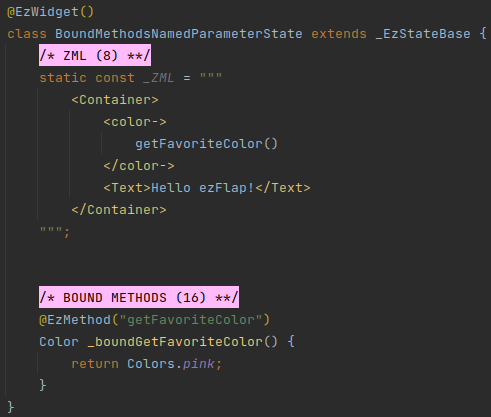
# Usage in Named Parameters
Named parameters accept a Dart expression.
Reference bound methods in these Dart expressions using the bound methods' Assigned Names.
# Example
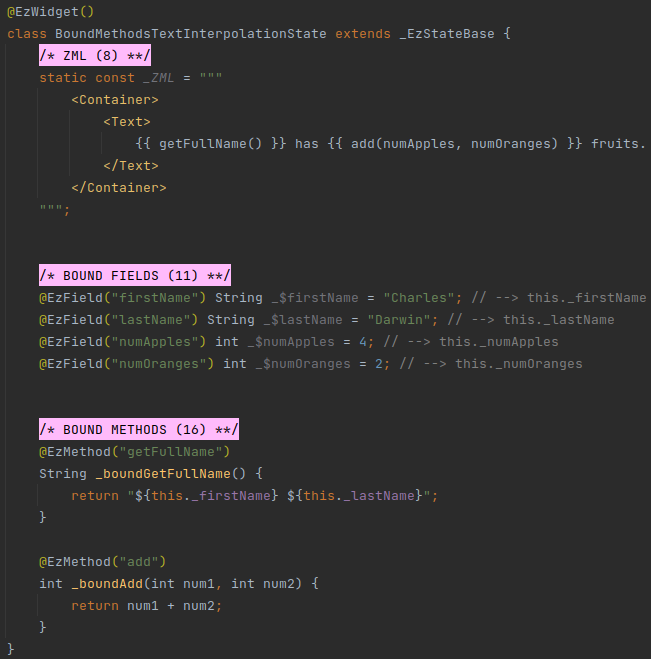
# Usage in Text Interpolation
Bound methods can be referenced inside mustache expressions ({{ }}) in a text block (i.e. in <Text>, or in
string attributes).
# Example
# Usage in Code
Bound methods can be invoked like any other method.
# Example